Abstract
介绍了直方图均衡化算法的具体流程,并使用代码实现了直方图均衡化。同时,与函数库中的直方图均衡化算法histeq进行比较。
Technical discussion
直方图均衡化是将原图像通过某种变换,得到一幅灰度直方图为均匀分布的新图像的方法。
直方图均衡化方法的基本思想是对在图像中像素个数多的灰度级进行展宽,而对像素个数少的灰度级进行缩减。从而达到清晰图像的目的。
步骤如下:
- 计算原始直方图的概率
统计每一个灰度在原始图像上的像素所占总体的比例,记为$P_i$。
- 计算直方图概率的累加值$s_i$
- 根据公式求取像素映射关系
找到原图像和均衡化图像灰度的对应关系,对原图进行操作,将每个像素映射成新的像素。
Discussion of results
图片0308.tif
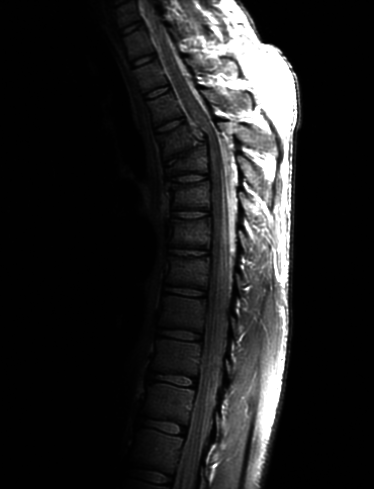
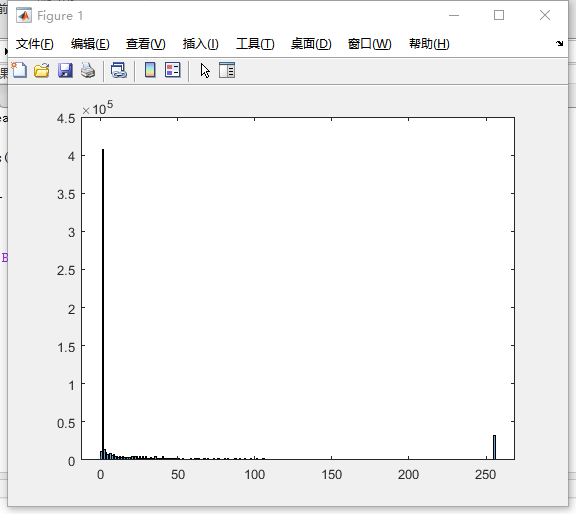
(a) Write a computer program for computing the histogram of an image.
思路:
枚举每个像素值,统计数量。
代码:
# 读入图像像素矩阵到mesh
mesh = imread("0308.tif");
# 统计每个像素值的数量
cnt = zeros(1, 256);
for i = 0 : 255
cnt(i + 1) = sum(sum(mesh(:, :) == i));
end
# 画出直方图
histogram('BinEdges', 0:256 ,'BinCounts', cnt)
运行结果:
(b) Implement the histogram equalization technique discussed in Section 3.3.1.
如第二页所示。
(c) Download Fig. 3.8(a) and perform histogram equalization on it.
代码(自己实现):
mesh = imread("0308.tif");
pr = zeros(1, 256);
siz = size(mesh);
n = siz(1);
m = siz(2);
for i = 0 : 255
pr(i + 1) = sum(sum(mesh(:, :) == uint8(i))) / (n * m);
end
sk = zeros(1, 256);
for i = 0 : 255
sk(i + 1) = round(255 * (sum(pr(1 : i + 1))));
end
newmesh = uint8(zeros(size(mesh)));
for i = 0 : 255
ind = find(mesh == i);
newmesh(ind) = sk(i + 1);
end
figure
subplot(1,2,1)
imshow(mesh)
title('原图')
subplot(1,2,2)
imshow(newmesh)
title('均衡化后')
figure
subplot(1,2,1)
imhist(mesh, 64);
title('原图像直方图');
subplot(1,2,2)
imhist(newmesh,64);
title('均衡化后的直方图');
实验结果:
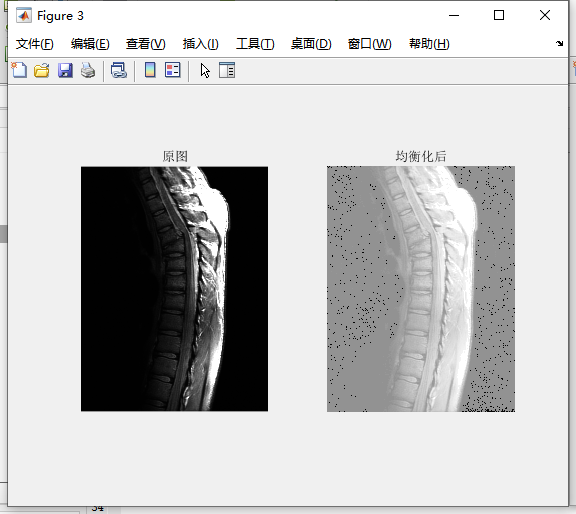
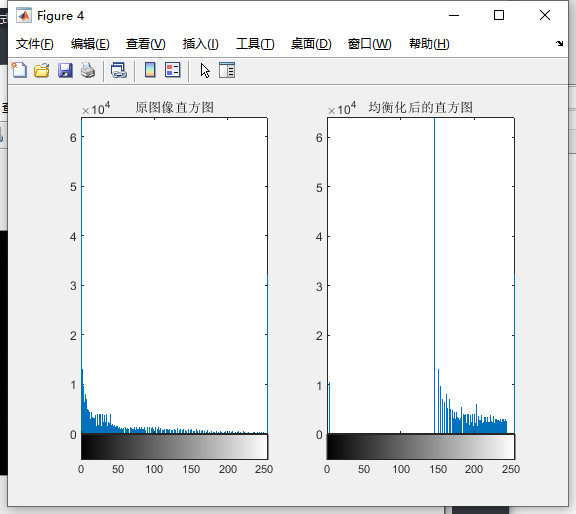
代码(使用函数库中的函数):
I=imread('0308.tif');
J=histeq(I); %直方图均衡化
figure,
subplot(121),imshow(uint8(I));
title('原图')
subplot(122),imshow(uint8(J));
title('均衡化后')
figure,
subplot(121),imhist(I,256);
title('原图像直方图');
subplot(122),imhist(J,256);
title('均衡化后的直方图');
实验结果:
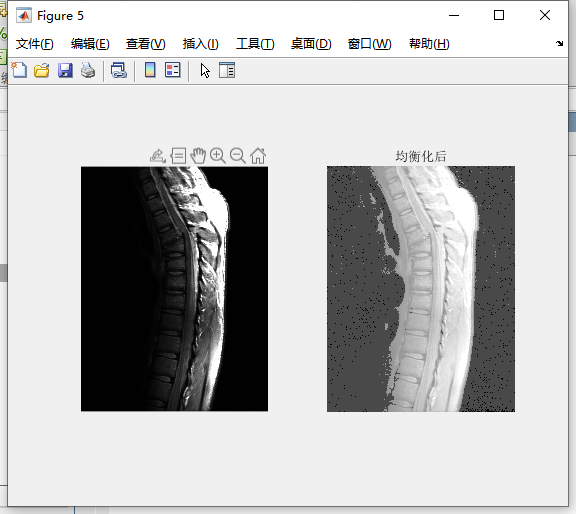
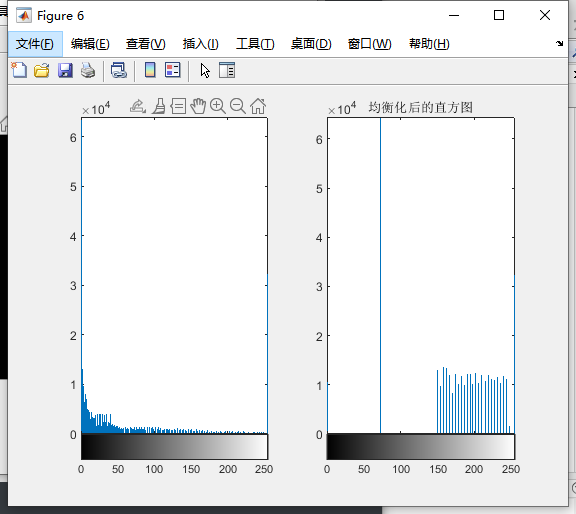
差异分析:
对于函数J = histeq(I,hgram)
当提供目标直方图 hgram时,histeq 选择灰度变换 T 以最小化
$c_0$ 是输入图像 I的累积直方图,$c_1$ 是 hgram 中所有强度 k 上的累积总和。这种最小化受以下条件的限制:
T必须单调- $c_1(T(a))$ 对 $c_0(a)$ 的过冲不能超过
a处直方图计数之间差距的一半。
histeq 使用变换 $b = T(a)$ 将 X(或颜色图)中的灰度级映射到其新值。
如果不指定 hgram,则 histeq 创建平坦的 hgram,
hgram = ones(1,n)*prod(size(A))/n;
然后应用前面的算法。
可以发现,这个直方图均衡化算法有条件限制的优化,区别于普通的直方图均衡化,因此图像增强效果会更好。